Circular Queue
Circular Queue is a linear data structure in which the operations are performed based on FIFO (First In First Out) principle and the last position is connected back to the first position to make a circle. It is also called ‘Ring Buffer’.
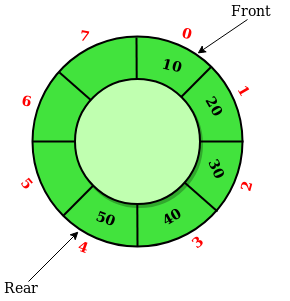
In a normal Queue, we can insert elements until queue becomes full. But once queue becomes full, we can not insert the next element even if there is a space in front of queue.
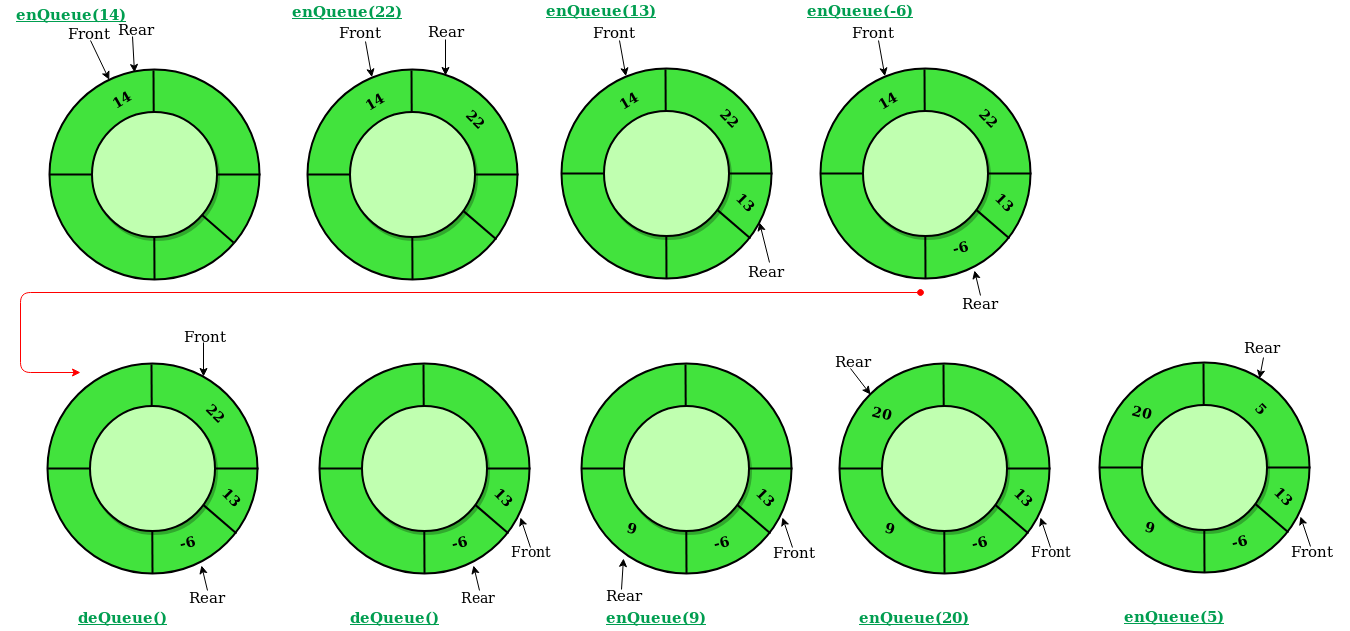
Operations on Circular Queue:
- Front: Get the front item from the queue.
- Rear: Get the last item from the queue.
- enQueue(value) This function is used to insert an element into the circular queue. In a circular queue, the new element is always inserted at the Rear position.
- Steps:
- Check whether queue is Full – Check ((rear == SIZE-1 && front == 0) || (rear == front-1)).
- If it is full then display Queue is full. If queue is not full then, check if (rear == SIZE – 1 && front != 0) if it is true then set rear=0 and insert element.
- deQueue() This function is used to delete an element from the circular queue. In a circular queue, the element is always deleted from the front position.
- Check whether the queue is Empty means check (front==-1).
- If it is empty then display Queue is empty. If the queue is not empty then step 3
- Check if (front==rear) if it is true then set front=rear= -1 else check if (front==size-1), if it is true then set front=0 and return the element.
C++
- Steps:


0 Comments